Introduction To Red Team
1. Red Team Operations
- A team-based exercise to simulate or emulate a genuine, real-life threat (TTPs) to an organisation to improve people, processes and technology.
- They’re given a specific goal:
- Demonstrating access to business-critical information, measure blue teams' detection & response policies.
- Identify gaps in the organisation’s defences, monitoring and incident response capabilities to reach that goal.
- Red Team Exercises focus on an end-to-end assessment of the entire organization.
- At the end of an engagement, Red Team will work with the organisation on how they can better detect and respond to such tactics and techniques in the future.
1.1 Red Team VS Penetration Test
| Red Teaming | Penetration Test |
|---|---|
| Have a clear objective defined by the organisation. | Focus on a single technology stack. |
| Emulate a real-life threat to the organisation. | The goals are to identify as many vulnerabilities as possible. |
| Look holistically at the overall security posture of an organisation. | Output is a report containing each vulnerability and remediation actions. |
| Put a heavy emphasis on stealth. | There is no explicit focus on detection or response. |
1.2 Technology, people, processes and procedural controls
When execute a phishing campaign:
- Technology: Maybe expecting the company has a mail gateway to put the email in the SPAM folder.
- People: How many employees were able to identify or discover the phishing campaign.
- Processes: When a user discover the phishing campaign, what process does the company has in place for employees to report the attack.
- procedural: When a user submit the mail to an analyst what procedural does the company has in place for the analyst to contain the attack.
2. Frameworks and Methodologies
- There are many Red Team frameworks availabe for public use.
- Red Teamers can use one of these frameworks as a strating point to design the scope of operation.
2.1 The Cyber Kill Chain
Advanced Persistent Threat:
- Advanced: The team who is very well focused and organized.
- Persistent: Establishes an illicit, long-term presence on a network.
- Threat: A person with intent, opportunity and capability to execute an operation.
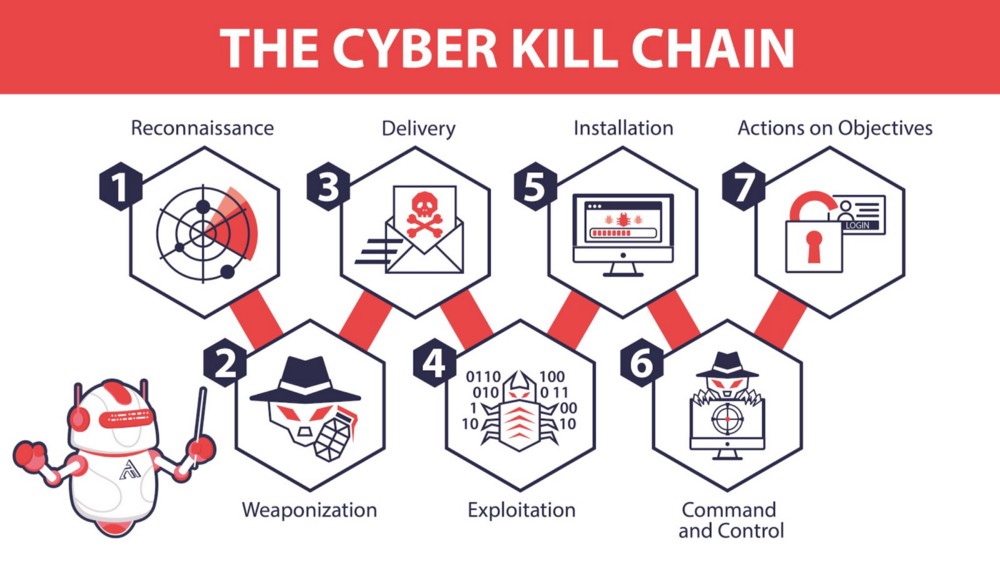
- Reconnaissance:
- Gather information about the target. Identify one person to target and then plan their avenue of attack.
- Weaponization:
- Create an attack that exploits vulnerabilities found in reconnaissance.
- Delivery:
- Select a delivery method after choosing which tools are best suited to exploit your vulnerabilities.
- Exploitation:
- The weapon has been delivered. The APT exploits a vulnerability on a system to get initial access.
- Installation:
- The APT installs a malware gain better access.
- Command and Control:
- The APT now set up persistent access to the target’s system for remote manipulation.
- Actions on Objectives:
- The APT achieve their intrusion objective. Ex: Data Exfiltration.
2.2 ATT&CK Framework - MITRE
- It has the phases of the attack as tactics.
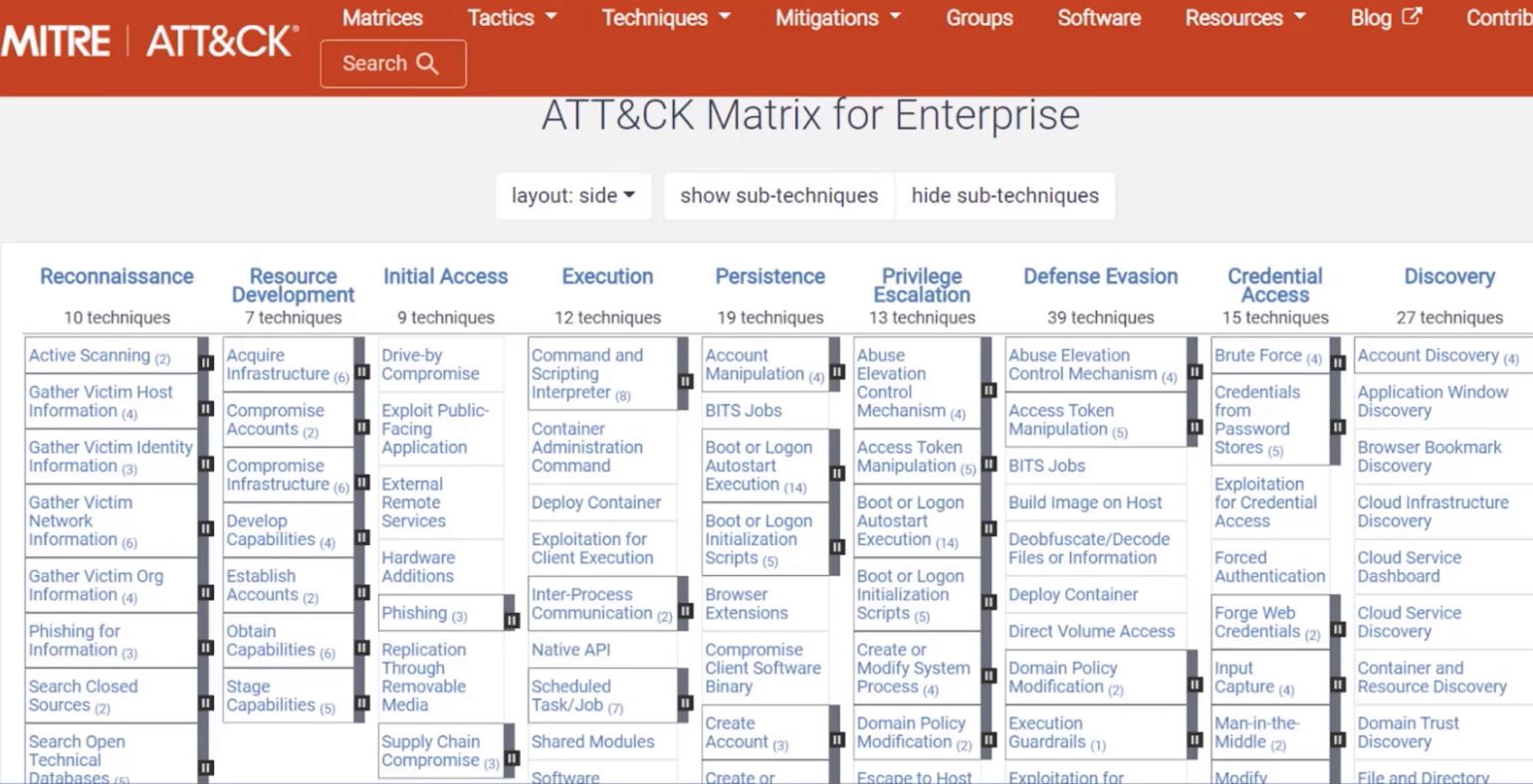
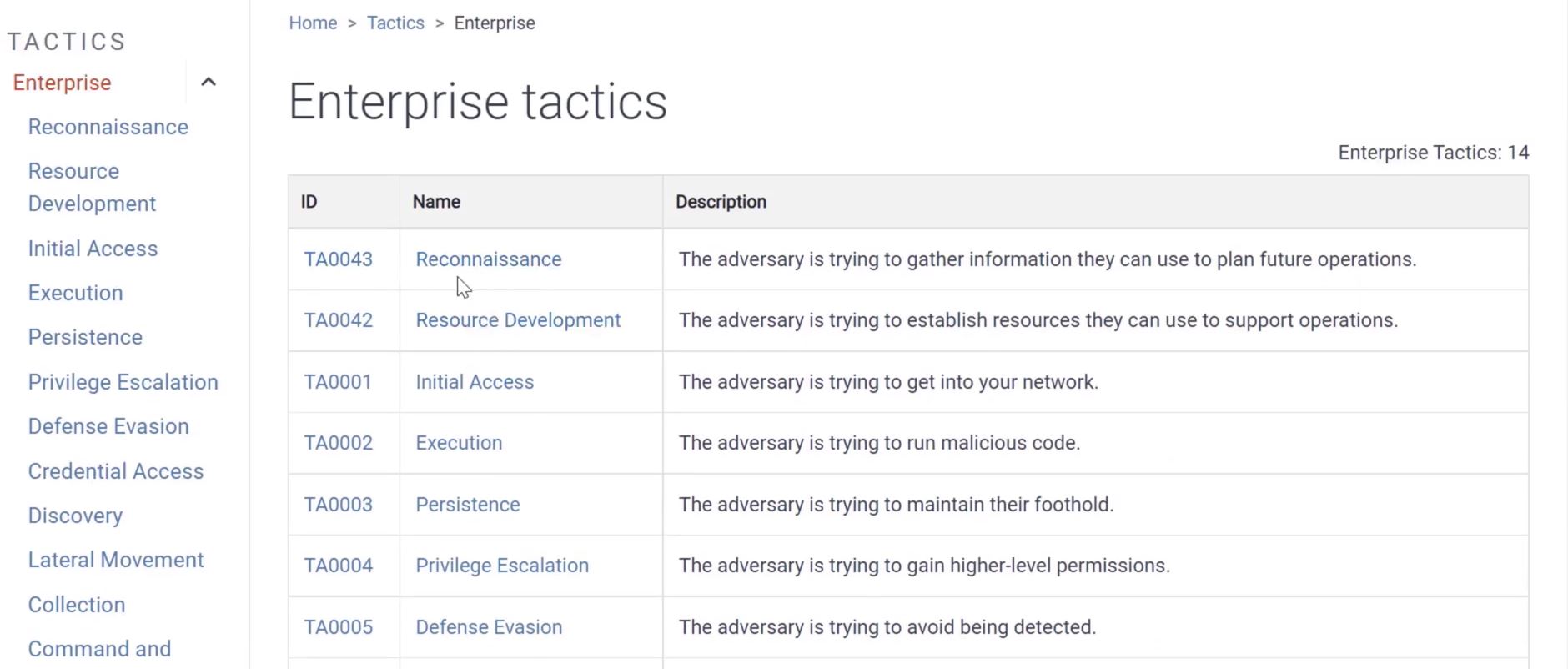
2.3 The Unified Kill Chain
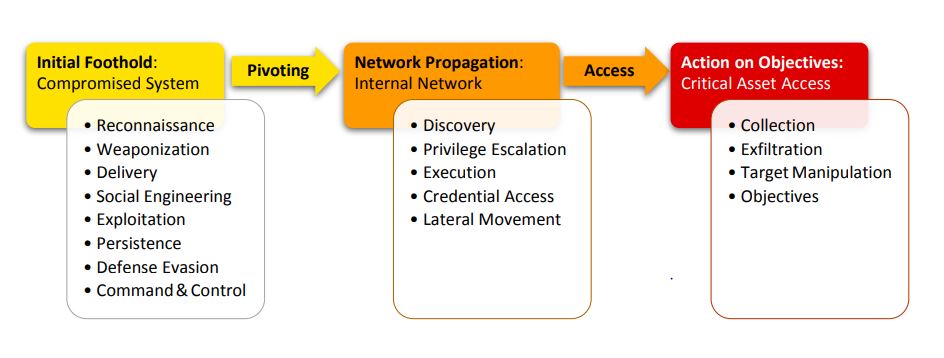
- Reconnaissance:
- Research, identification, and selection of targets using active or passive reconnaissance.
- Weaponization:
- Coupling a remote access trojan with an exploit into a deliverable payload.
- Defense Evasion:
- Techniques may use for evading detection or avoiding defenses.
- Delivery:
- Transmit the payload to the targeted environment.
- Exploitation:
- Exploit vulnerabilities in systems.
- Persistence:
- Maintaining access to a compromised machine.
- Command & Control:
- Communicate with controlled systems.
- Pivoting:
- Tunneling traffic through controlled system.
- Privilege Escalation:
- Gain a higher permissions on a system.
- Discovery:
- Gain knowledge about a system and its internal network.
- Lateral Movement:
- Access and control remote systems on a network.
- Execution:
- Execute code on a local or remote system.
- Credential Access:
- Access or control over system, service or domain credentials.
- Target Manipulation:
- Manioulate of the target system to achive the objective of the attack.
- Collection:
- Identify and gather information from a target network prior to exfiltration.
- Exfiltration:
- Remove, collect files and information from a target network.
3. Red Team Exercise Phases
The hybrid approach is:
- Threat Intelligence
- Planning
- Testing
- Closure
3.1 Threat Intelligence
The Red Team Exercise starts with a Threat Intelligence phase.
- The Threat Intelligence analyses and reviews applicable threat intelligence and uses this information to develop scenarios and draft a penetration test plan.
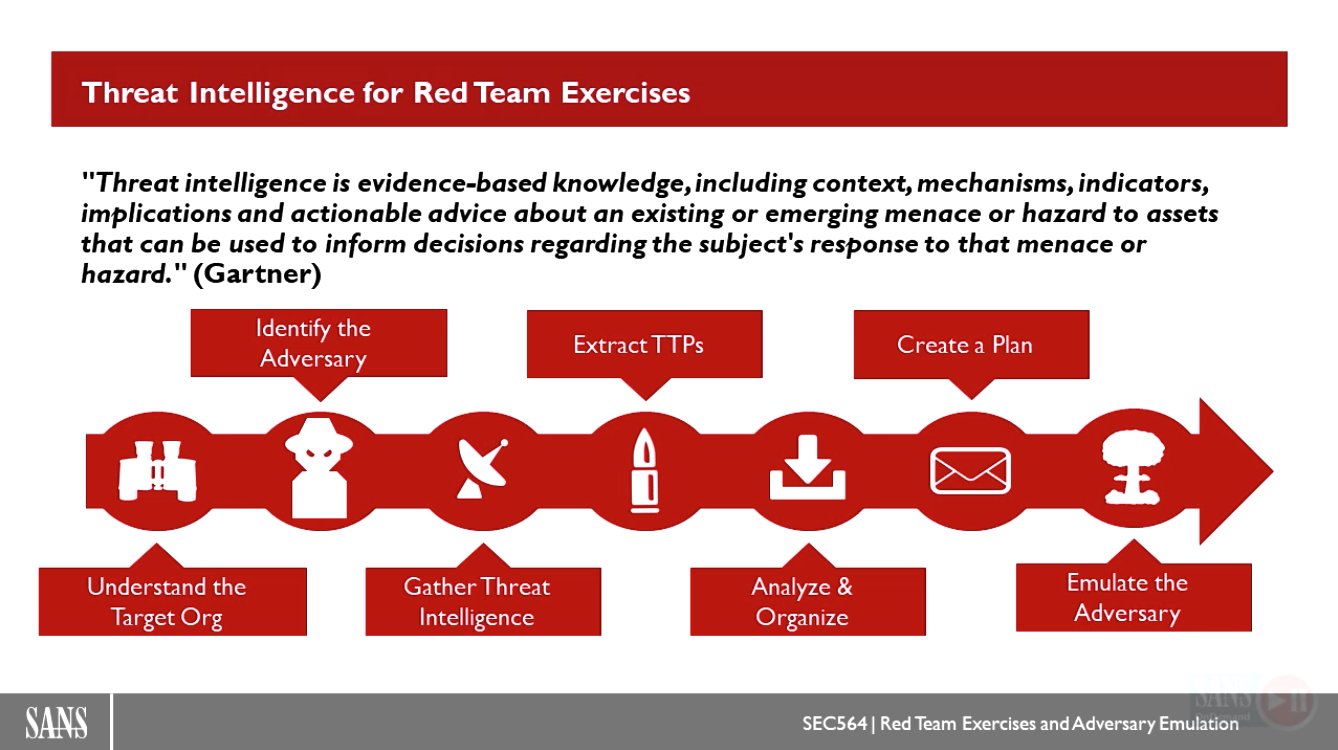
- Understand the target Organization
- Very Important to understand the target Organization.
- Identify the Adversary want to emulate
- Depending on the target, should consider the adversary’s capability, intent and opportunity.
- If the taregt is new to Adversary Emulations, start with the lower actors.
- Gather Threat Intelligence about the Adversary
- Extract TTPs
- Start at the tactical level with the adversary techincal goal and move to the techniques.
- Analyz and Organize
- After extracting the TTPs, match them to a framework.
- Create an Adversary Emulations Plan
- Emulate the Adversary
- The Red Team Exercise execution begins.
3.2 Planning phase
It covers test preparation activities. This is to ensure risks are managed and test objectives are achieved.
- Triggers:
- When and why is a Red Team Exercise being requested?
- Objectives:
- What are the objectives of the Adversary Emulation?
- Scope:
- Scenario, TTPs and Metrics
- Trusted Agents:
- A limited number of stakeholders aware of the exercise.
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Rules of Engagement
3.3 Testing phase
-
Red Team Planning
- Fill any planning gaps
- Attack Infrastructure
- Setting up infrastructure should begin as early as possible.
- The infrastructure should never be used for more than exercise.
- The steps a team should take to build an Attack Infrastructure:
- Choose external hosting service providers. Ex: AWS
- Purchase domain names.
- Generate domain certificates.
- Setup mail servers.
- Setup phishing and credential theft sites.
- Setup long and short Haul C2.
- Configure custom C2 tooling.
- Test external C2 communication.
- Reconnaissance
- Focused on specific items to obtaining initial access.
- Social Engineering
- Weaponization
- Create payloads and document the IoC that the attack will have.
-
Initial Access / Foothold
-
Network Propagation
-
Action on Objective
3.4 Closure
Is one of the most important phases of the framework. The red team should ensure that:
- All data and logs were saved and securely stored.
- All systems should be cleaned up and left how they were originally found.