Initial Access
It represents the techniques adversaries may use to gain an initial foothold within a network. One of the most complex and time-consuming aspects of a red team operation. It may be accomplished via various methods:
-
Exploitation:
- Drive-by Compromise: Exploiting a user visiting a website.
- Exploit Public-Facing Application.
- External Remote Service: Exploit or find a valid account for services like VPNs, Citrix..etc.
-
Hardware:
- Through Removable Media.
-
Phishing:
- Spear Phishing Attachment
- Spear Phishing Link
- Spear Phishing via Service: Use of third-party services.
-
Supply Chain Compromise:
- Manipulate products or product delivery mechanisms prior to receipt by a final consumer for the purpose of data or system compromise. Ex. SolarWinds
-
Trusted Relationship:
- Breach or leverage organizations that have access to intended victims.
-
Valid Accounts:
- May have access using capture credentials got earlier in the reconnaissance phase.
- Or using an account provided by the company.
1. Initial Access Phases
- Reconnaissance
- Build an attack infrastructure
- Weaponize payloads
- Social Engineer to deliver payload
- Exploit a system to gain access
1.1 Reconnaissance
Research, identification, and selection of targets using active or passive reconnaissance.
- The team uses this phase to collect and process information about the target organization, the industry it operates in and the target landscape of specific countries where the organization operates.
- Once the team understands the organization, they can then identify and classify the types of adversary(s) most likely to attack the organization.
- The team then analyzes and organizes the TTPs being use with adversaries.
- The team uses this data to execute better reconnaissance activities.
- Should have a better understanding of the target’s:
- Network architecture: Domain names, DNS.
- IP Space: IP Addresses owned and live hosts.
- Technology Solutions: OSs, Servers, client application.
- Email format and infrastructure.
- Security Proccedures: Controls need to bypass.
- People and culture.
1. Passive Reconnaissance
- The team uses passive reconnaissance techniques to gather information without actively interacting with the target organization’s systems.
- Places to look for phishing:
- Departement heads (HR, C-Level)
- Information from Job Postings:
- Software
- Vendor
- Appliance information
- Credentials from previous/unknown data breaches.
- pwndb: A tool for searching leaked credentials using the Onion service with the same name.
- pwnedOrNot: A tool for finding passwords of compromised email accounts using haveibeenpwned API.
2. Active Reconnaissance
-
The team uses active reconnaissance techniques to gather information either directly or indirectly interacting with the target organization’s systems.
-
Some of the information need to be gathered:
- Company websites
- Network block
- DNS information
- Domian name(s)
- Subdomain names
-
Mail Infrastructre information:
- SPF
- DKIM
- DMARC
- PTR
-
Some website/Tools that can be used the passive and active reconnaissance:
- Phonebook: Collect emails and domains.
- Hunter: Collect emails.
- ViewDNS: Collect DNS information.
- Shodan: Collect information about the target.
- ZoomEye: Like Shodan, Collect information about the target.
- Spyse: Like Shodan, Collect information about the target.
- Spiderfoot: Open source intelligence (OSINT) automation tool.
- theHarvester: Gather emails, names, subdomains and IPs.
- SpoofCheck: Checks SPF and DMARC records for weak configurations that allow spoofing.
1.2 Attack Infrastructure
Techniques that involve adversaries creating, purchasing or compromising resoureces that can be used to support targeting.
- Some of activities in thi phase is:
- Purchasing VPS hosts
- Purchasing domain names
- Setting up mail servers
- Researching sites to target for phishing campaigns
- Build a C2 infrastructre, need to implement:
- Redirectors
- Domain fronting
- Web Categorization
- SPF, DKIM, DMARC for SMTP servers
1. Redirectors
-
Are pivots used to separate communication between a target and C2 servers. - It’s easier to setup a new redirector than a new c2 infrastructure.
-
They provide obfuscation for the backend servers and confuse the blue team from investigating the traffice.
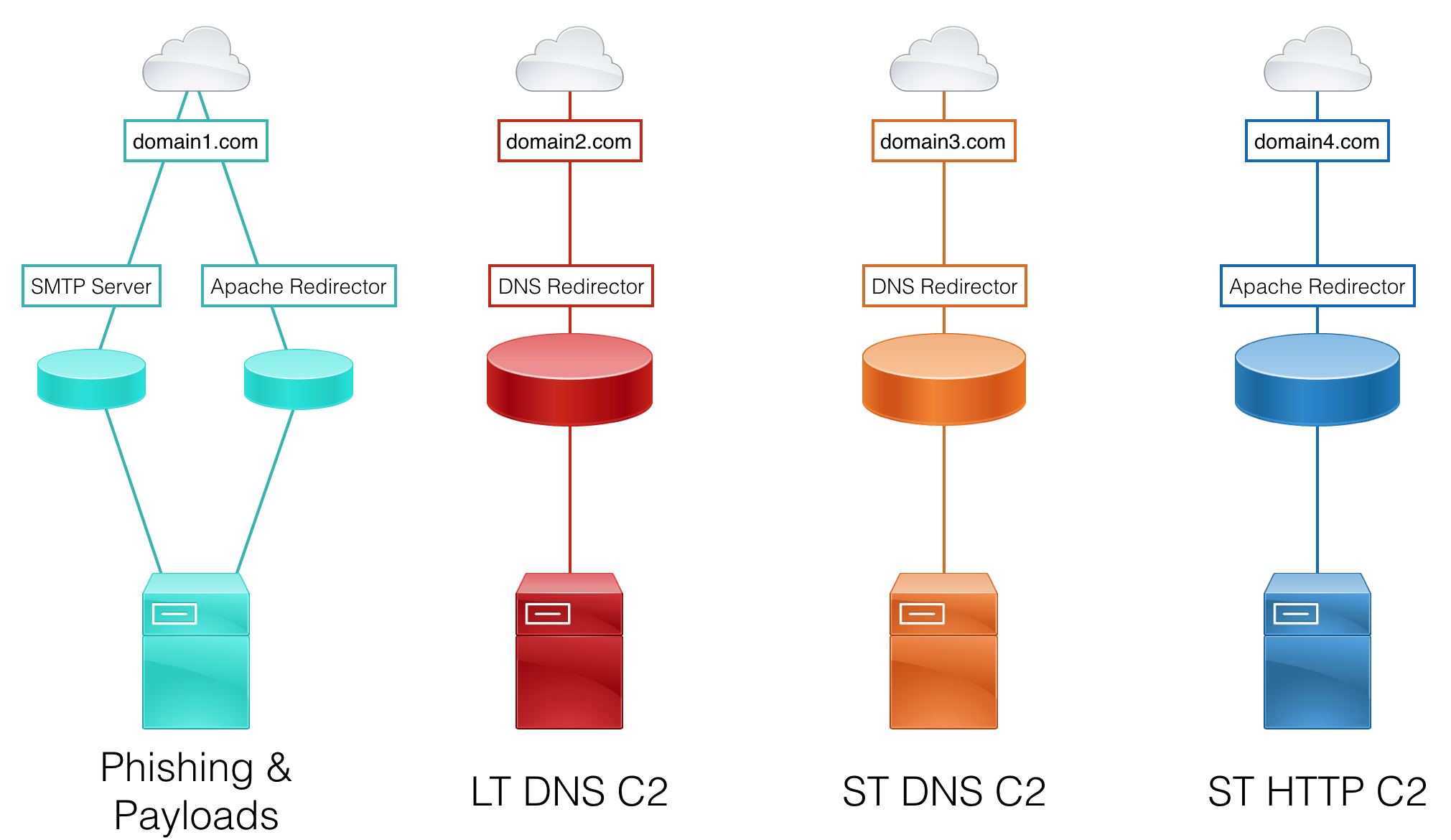
-
Redirectors Types:
- SMTP to strip off any traces of original email (SRC IP, Cliend Headers).
- Payloads
- Specific traffic (HTTP/s, DNS, etc)
2. Domain Fronting
- A technique used to route traffic through CDN (Content Delivery Network) platforms (Google App Engine, Amazon CloudFront, Azure).
- It can be used to solve the issue of categorisation and domain reputaion.
- It’s very difficult to detect as numerous legitimate application are using it.
3. Web Categorization
- Most organizations don’t allow outbound access directly to IP Addresses.
- Some outbound proxies block domains based on categories.
- All domains should be categorized prior to test execution.
- Websites that can be used to purchase categorized domain names that have expired:
4. SMTP Server
- Should use a disposable VPS for sending mails.
- Cobalt Strike can use remote SMTP servers for phishing.
1.3 Weaponization
- Is the coupling of a remote access method into a deliverable payload.
- A PDF or a Microsoft Office documents as the weaponized deliverable for the malicious payload.
- It is a part of Red Team planning and Preparation.
- The payload created must be configured to connect back via the C2 channels.
1.1 Blend In
- Most organizations have controls around blocking standard windows executables (*.exe).
- Red team will rely on built-in Windows utilities to execute the payload.
- Visual Basic
- JavaScript
- HTA
- Powershell
- WMIC
- MSBuild
- RegSrv32
1.4 Delivery
- Select a delivery method after choosing which tools are best suited to exploit your vulnerabilities.
1. OLE
- A very common technique for delivering payloads is Object Linking and Embedding.
- Allows you to embed files within Office documents, which ultimately get executed on activation (double click).
2. Email
- Email delivery is a common method, whether sending a phishing email with a link or an attachement.
3. Web
- Can host a web server with the payload for the target to download and execute.
- Need to socially engineer the target to download and execute the payload.
- Need to purchase a domain, hosting in a cloud and obtain reputation of the domain.